 Whether you’re new to industrial automation or a seasoned professional, questions about industrial sensors often arise. This FAQ covers the most common inquiries regarding sensor types, applications, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Whether you’re new to industrial automation or a seasoned professional, questions about industrial sensors often arise. This FAQ covers the most common inquiries regarding sensor types, applications, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
1. What Are the Main Types of Industrial Sensors?
Industrial sensors come in many varieties, including:- Proximity Sensors: Detect presence or absence of objects without contact.
- Photoelectric Sensors: Use light to detect objects, distance, or color.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Use sound waves for distance and level measurement.
- Laser Displacement Sensors: Provide high-precision distance measurement.
- Temperature Sensors: Measure temperature using thermocouples or RTDs.
- Pressure Sensors: Monitor fluid or gas pressure in systems.
2. How Do I Choose the Right Sensor for My Application?
Consider these factors:- The physical property to measure (distance, presence, temperature, etc.)
- The environment (dusty, wet, high temperature)
- Required accuracy and response time
- Compatibility with your control system (analog, digital, communication protocols)
- Installation space and mounting options
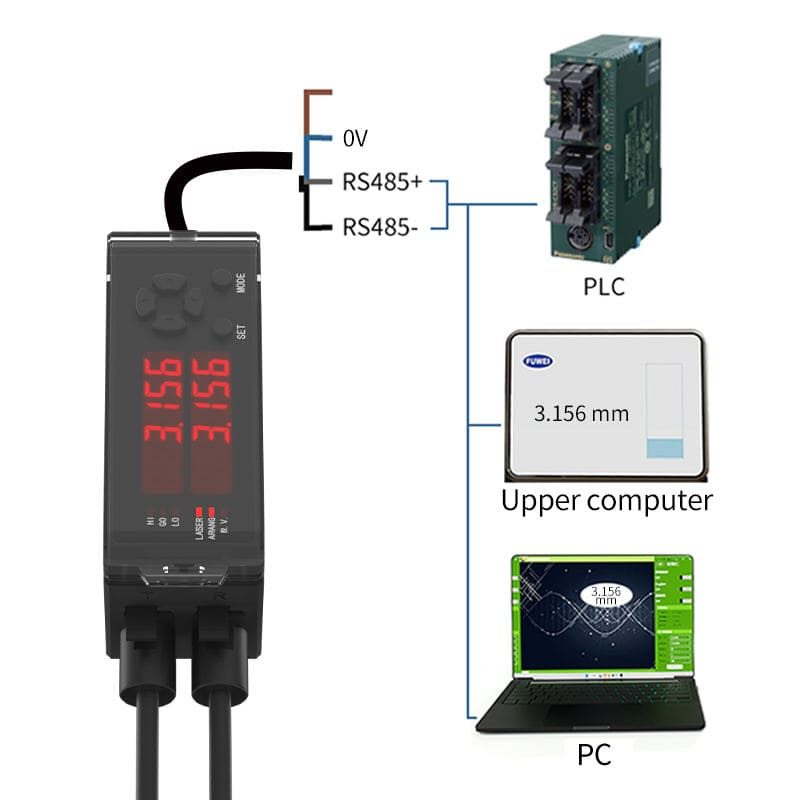
3. What Are Common Communication Protocols for Sensors?
Common protocols include:- Analog Outputs: 0–10 V, 4–20 mA signals
- Digital Outputs: NPN, PNP switching signals
- Serial Communication: RS485, Modbus, IO-Link
- Industrial Ethernet: PROFINET, EtherCAT
4. How Often Should Sensors Be Calibrated?
Calibration intervals depend on sensor type and usage. Critical measurement applications may require calibration every 6–12 months, while less sensitive applications can extend intervals. Follow manufacturer recommendations and monitor sensor accuracy over time.5. What Are Typical Causes of Sensor Failure?
- Mechanical damage or misalignment
- Environmental contamination (dust, oil, moisture)
- Electrical issues such as wiring faults or power surges
- Calibration drift or component aging
6. Can Industrial Sensors Work in Harsh Environments?
Yes, many Industrial sensors are designed with robust housings, high IP ratings (IP67, IP68), and special coatings to withstand dust, moisture, chemicals, and temperature extremes.7. How Do I Troubleshoot a Sensor That Is Not Working?
Try the following steps:- Check power supply and wiring connections.
- Verify sensor alignment and cleanliness.
- Test sensor output with a multimeter or diagnostic tool.
- Refer to the manufacturer’s manual for error codes or LED indicators.
- Replace the sensor if it is physically damaged or fails functional tests.
8. What Is the Difference Between Analog and Digital Sensors?
Analog sensors provide continuous output signals proportional to the measured value, suitable for detailed analysis. Digital sensors give discrete ON/OFF outputs or communicate via protocols, ideal for presence detection and smart integration.9. Are Customized Sensors Available?
Yes, many manufacturers, including FUWEI, offer OEM/ODM customization, such as tailored measurement ranges, special connectors, or branded packaging to meet specific industrial needs.10. Where Can I Buy Reliable Industrial Sensors?
Look for experienced manufacturers with proven quality, certifications (ISO, CE), comprehensive technical support, and global shipping capabilities. FUWEI is a trusted partner offering a wide range of sensors suitable for diverse industrial applications.Need More Help?
If your question isn’t covered here, or you want personalized advice, feel free to contact our experts. Contact FUWEI Sensor Specialists →Tags: Industrial sensors FAQ, sensor troubleshooting, sensor types, factory automation sensors, FUWEI sensors




Leave a Message